Cash flow forecasts 2.1.4
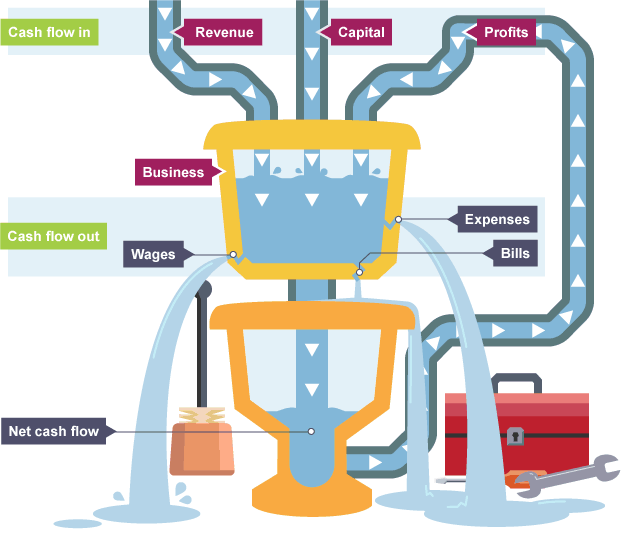
Cash flow forecast - is a statement of the expected cash inflow coming from the sales revenue and expected cash outflow needed to cover production costs. The difference between the inflow and the outflow is the net cash flow, a crucial indicator of the ability of a business to cover its day-to-day running costs.
Cash flow is important to a business as it needs it to ensure a positive cash balance in order to meet day to day expenses. It roughly estimates cash flow for up to about two years into the future.
The forecast will help potential lenders (including banks) to see what the likely financial needs of the business will amount to.
Opening Balance = what is in the bank on the first day of the month
Total cash inflow = all cash entering the business in that month
Total cash outflow = all cash leaving the business in that month
Net cash flow = Total cash inflow - Total cash outflow
Closing balance = Opening balance + Net cash flow
FIGURES IN BRACKETS MEAN MINUS FIGURES
INTERPRETING A CASH-FLOW FORECAST
By monitoring the closing balance, the business can see how much cash they have at the bank on a monthly basis. If the closing balance is a negative figure, then that is a prompt to seek extra finance, either in the form of an overdraft or a loan.
An overdraft allows a business to spend more than it has in its accounts, up to an agreed limit. This is a flexible and useful form of finance that is particularly suited to cash flow problems. Interest is only paid on the amount borrowed, for the time it is used.
A loan will be a fixed amount with a lower interest rate than the overdraft, but if the business has insufficient working capital it may be the best approach.
If a cash flow problem can be foreseen, then it may be possible to plan ahead and reduce the payments going out, perhaps by asking creditors (to whom money is owed) to wait another month or so before payment. For example, advertising could be postponed. It may also be possible to persuade debtors (who owe the business money) to pay up early to increase cash coming in.
By changing figures in the cash flow forecast, different scenarios can be examined, e.g. the impact of a rise in costs. Plans can then be made to deal with the problem.
Most businesses find that the cash outflow is high in the early months after start-up. There will be a time lag before the cash inflows from sales revenue build up. When the business buys raw materials or pays wages, there is a cash outflow. When it sells its products, there is a cash inflow.
Cash dries up and creditors demand payment. Bills need to be paid on a regular basis. If you cant pay your bills, you cant stay in business.
Therefore managing cash flow is crucial. A cash flow forecast helps to protect when extra finance will be needed to avoid these problems.
HOW TO CONSTRUCT A CASH FLOW FORECAST
STEP 1 : Forecast cash inflows
STEP 2 : Forecast cash outflows
FACTORS AFFECTING CASH FLOW
CASH INFLOW
CASH OUTFLOW
LIMITATIONS OF A CASH FLOW FORECAST
Cash flow is important to a business as it needs it to ensure a positive cash balance in order to meet day to day expenses. It roughly estimates cash flow for up to about two years into the future.
The forecast will help potential lenders (including banks) to see what the likely financial needs of the business will amount to.
CALCULATING CASH FLOW
Opening Balance = what is in the bank on the first day of the month
Total cash inflow = all cash entering the business in that month
Total cash outflow = all cash leaving the business in that month
Net cash flow = Total cash inflow - Total cash outflow
Closing balance = Opening balance + Net cash flow
FIGURES IN BRACKETS MEAN MINUS FIGURES
INTERPRETING A CASH-FLOW FORECAST
By monitoring the closing balance, the business can see how much cash they have at the bank on a monthly basis. If the closing balance is a negative figure, then that is a prompt to seek extra finance, either in the form of an overdraft or a loan.
An overdraft allows a business to spend more than it has in its accounts, up to an agreed limit. This is a flexible and useful form of finance that is particularly suited to cash flow problems. Interest is only paid on the amount borrowed, for the time it is used.
A loan will be a fixed amount with a lower interest rate than the overdraft, but if the business has insufficient working capital it may be the best approach.
If a cash flow problem can be foreseen, then it may be possible to plan ahead and reduce the payments going out, perhaps by asking creditors (to whom money is owed) to wait another month or so before payment. For example, advertising could be postponed. It may also be possible to persuade debtors (who owe the business money) to pay up early to increase cash coming in.
By changing figures in the cash flow forecast, different scenarios can be examined, e.g. the impact of a rise in costs. Plans can then be made to deal with the problem.
Most businesses find that the cash outflow is high in the early months after start-up. There will be a time lag before the cash inflows from sales revenue build up. When the business buys raw materials or pays wages, there is a cash outflow. When it sells its products, there is a cash inflow.
Cash dries up and creditors demand payment. Bills need to be paid on a regular basis. If you cant pay your bills, you cant stay in business.
Therefore managing cash flow is crucial. A cash flow forecast helps to protect when extra finance will be needed to avoid these problems.
HOW TO CONSTRUCT A CASH FLOW FORECAST
STEP 1 : Forecast cash inflows
- Owner's investment or other source of finance
- Cash sales estimated from sales forecast
STEP 2 : Forecast cash outflows
- Payment of fixed costs (these should be easy to estimate on a month to month basis)
- Time delay between estimates and signing contracts can cause inaccuracies
- Payment of variable costs
- If sales are difficult to forecast, so are the costs associated with meeting demand.
- Made more difficult if suppliers are free to change the selling price
- Unforeseen expenses or One off payments that are not expected or expenses that have not been planned for
- Payment terms (What if a supplier changes terms and wants payment sooner or a lender demands their money back)
FACTORS AFFECTING CASH FLOW
- Timings of cash inflows and outflows
CASH INFLOW
If cash inflows are slow this may cause cash flow
problems
A firm may try to speed up cash inflows
This may include offering a discount for early
payment or penalties for late payments
Businesses may need to chase customers for
payment i.e. credit control
When a business is owed money from customers
these are referred to as receivables
CASH OUTFLOW
If cash outflows are too quick this may cause
cash flow problems
A firm may try to slow down cash outflows
This may include negotiating longer payment
terms from suppliers
When a business owes money to suppliers these are
referred to as
- Like all forecasts, they may be prone to error
- The further ahead you try and look, the less accurate the forecast becomes
- Careful planning cannot take into account all the possibilities that may arise
- The cost of the materials may increase
- Consumer tastes may change
- Competitors may bring out new products
- The external economy can also limit the accuracy and usefulness of a forecast; the business cycle alters the demand; interest rates and tax rates may change; exchange rates may affect a business if it exports or imports; supplier goes out of business
- Market research which forecast is based on may have been inaccurate, biased or flawed
- Demand may be over or under estimated
Comments
Post a Comment