Economic Influences - Inflation 2.5.1
Inflation - A sustained increase in the general level of prices within an economy, there is a fall in the value of money. It is measured by recording price changes for a wide range of goods and services likely to be bought by average families.
Consumer price index - A measure that examines the weighted average of prices of a basket of consumer good/ services.
Disinflation - This is when a lower inflation rate causes prices to rise more slowly
Deflation - A decline in the general price level in an economy, characterised by an inflation rate that is lower than 0%
Hyperinflation - A period of very high inflation rates, usually leading to a loss of confidence in an economy's currency
Inflation rate - The annual rate of change of the average price of goods and services
Inflation can be a serious problem. it creates uncertainty and instability because it is hard to know whether it will accelerate or slow down. It is measured by the annual percentage change in consumer prices
The UK government has set an inflation target of 2% using the consumer price index. This will help the economy to grow steadily without creating problems.
The Bank of England's (BOE) Monetary Policy Committee is responsible for controlling the rate of inflation and making sure inflationary pressures are controlled and the inflation target is reached over a two year time period. It does this by adjusting the base rate of the interest in order to affect interest rates across the economy.

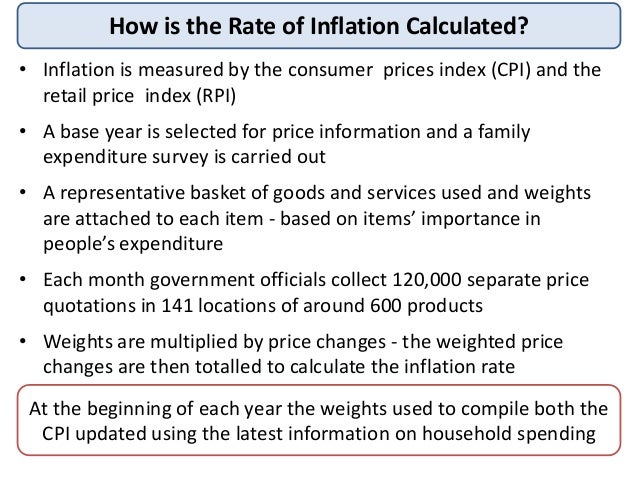

Consumer price index - A measure that examines the weighted average of prices of a basket of consumer good/ services.
Disinflation - This is when a lower inflation rate causes prices to rise more slowly
Deflation - A decline in the general price level in an economy, characterised by an inflation rate that is lower than 0%
Hyperinflation - A period of very high inflation rates, usually leading to a loss of confidence in an economy's currency
Inflation rate - The annual rate of change of the average price of goods and services
Inflation can be a serious problem. it creates uncertainty and instability because it is hard to know whether it will accelerate or slow down. It is measured by the annual percentage change in consumer prices
The UK government has set an inflation target of 2% using the consumer price index. This will help the economy to grow steadily without creating problems.
The Bank of England's (BOE) Monetary Policy Committee is responsible for controlling the rate of inflation and making sure inflationary pressures are controlled and the inflation target is reached over a two year time period. It does this by adjusting the base rate of the interest in order to affect interest rates across the economy.
A FALL IN INFLATION IS NOT THE SAME AS PRICES FALLING
(only when there is DEFLATION will the general price level fall)


INFLATION CAN AFFECT BUSINESSES
- It is hard to plan for the future when there is uncertainty regarding future costs. This may make businesses less likely to invest
- Inflation may mean that the costs of supplies and wages are rising. This can reduce profitability unless the business can raise prices. However, higher prices may lead to a fall in sales.
- If UK businesses face a higher rate of inflation than their foreign competitors, UK costs may rise faster. If they try to maintain profit level by raising prices, they will lose competitiveness and face falling export sales.
- Imports from countries with lower rates of inflation may increase and take sales away from UK business.
- Inflation reduces the value of money, so repaying loans is easier if inflation is high. BUT if interest rates are raised due to inflation, the cost of borrowing increases. This makes businesses less likely to invest and grow.
- Higher interest rates mean consumers face increased credit changes and mortgage payments. They will all spend less; sales revenue will tend to fall.
Comments
Post a Comment