Stock control and Interpretation of stock control diagram - 2.4.3
Stock control - stock is a current asset held by business to help meet the demand of customers
Stock can be held in 3 forms:
The amount of stock held will depend upon:
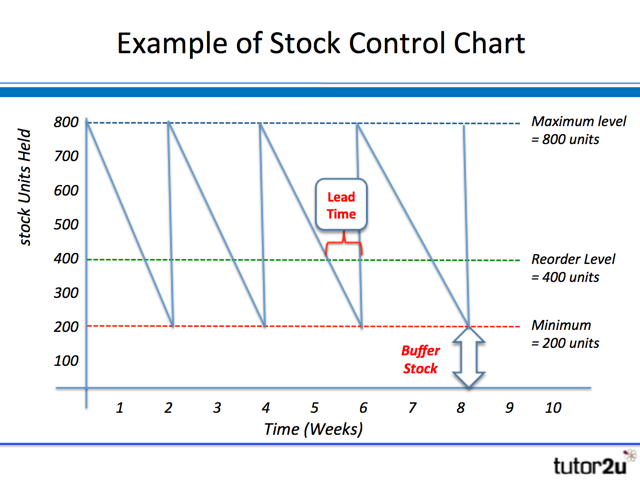
STOCK CONTROL DIAGRAM - A managment tool used to control and monitor the flow of stock
LEAD TIME - The time it takes between placing an order and receiving delivery. The GREATER the lead time, the HIGHER the minimum stock level.
RE-ORDER LEVEL - The level of stock which triggers and order, this may be done automatically by a computerised system. The re-order level will be determined by both the lead time and the minimum stock level.
BUFFER STOCK LEVEL OF STOCK - Stock held by a business to cope with unforeseen circumstance e.g. sudden increase in demand, break down in supplies. When a business reaches its minimum stock level it is left just with buffer stock. A business operating JIT system will have zero buffer stock
RE-ORDER QUANTITIES - The point at which an order for new stock is placed, this will be dependent on buffer level of stock and lead time. A computerised stock control system will automate this process so that when stock reaches this level, an order is automatically sent to a supplier.
DISADVANTAGES OF HOLDING BUFFER STOCK
Lost stock = Damaged profit margins due to fixed/variable costs not being covered by revenue = budgets being affected and restricted for the next year.
Under-utilisation of other resources e.g. labour and machinery stand idle
Wasting resources e.g. money, space, time
Running out of stock (stock-out) = Can't fulfil customer requirements = customer dissatisfaction = refunds if payment has already been taken = brand reputation damaged = customer buys from competitors increasing their sales = loss of competitiveness
Stock can be held in 3 forms:
- Raw materials
- Work in progress
- Finished products
The amount of stock held will depend upon:
- the business' attitude to risk (Hate risk = large buffer stock) (Love risk = small buffer stock)
- the importance of speed of response as an operational objective
- speed of change within the market
- nature of the product e.g. perishable or long lasting
LEAD TIME - The time it takes between placing an order and receiving delivery. The GREATER the lead time, the HIGHER the minimum stock level.
RE-ORDER LEVEL - The level of stock which triggers and order, this may be done automatically by a computerised system. The re-order level will be determined by both the lead time and the minimum stock level.
BUFFER STOCK LEVEL OF STOCK - Stock held by a business to cope with unforeseen circumstance e.g. sudden increase in demand, break down in supplies. When a business reaches its minimum stock level it is left just with buffer stock. A business operating JIT system will have zero buffer stock
RE-ORDER QUANTITIES - The point at which an order for new stock is placed, this will be dependent on buffer level of stock and lead time. A computerised stock control system will automate this process so that when stock reaches this level, an order is automatically sent to a supplier.
REORDER LEVEL = MAX LEVEL - MIN LEVEL
ADVANTAGES OF HOLDING BUFFER STOCK
- Helps when demand increases unexpectedley, business can dip into buffer stock rather than running out of stock and losing customers to competitors.
- If lead time is not always consistent due to supplier unreliability, then the business can dip into the buffer stock while waiting for delayed delievery
- Potential for lower unit costs by ordering in bulk/high quantities
- Less likelihood of "stock outs"
DISADVANTAGES OF HOLDING BUFFER STOCK
- Large stock holdings are costly making fixed costs larger e.g. storage
- Larger risk of stock obsolescence, especially if the business solely produces products that are perishable (e.g. fruit)
- More capital is tied up in working capital - can be used elsewhere in the business
- Not being "lean", so could explore other ways of utilising lean production techniques
Lost stock = Damaged profit margins due to fixed/variable costs not being covered by revenue = budgets being affected and restricted for the next year.
Under-utilisation of other resources e.g. labour and machinery stand idle
Wasting resources e.g. money, space, time
Running out of stock (stock-out) = Can't fulfil customer requirements = customer dissatisfaction = refunds if payment has already been taken = brand reputation damaged = customer buys from competitors increasing their sales = loss of competitiveness
Comments
Post a Comment